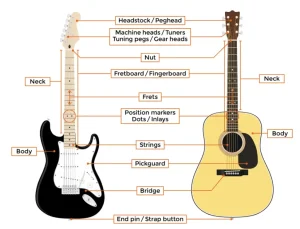
Playing classical guitar requires not only musical knowledge, but also a deep understanding of proper technique to produce beautiful and accurate sounds. This article will cover the main aspects of classical guitar technique, including hand position, body position, and guitar maintenance, drawing from a variety of sources, including the book “Pumping Nylon” by Scott Tennant.


Hand Technique
Proper hand technique is crucial for achieving good tone and accuracy when playing classical guitar. The right hand should rest on the bridge of the guitar, with the thumb positioned behind the fingers. The fingers should be curved and rest on the strings, with the fingertips making contact with the string. This position allows for precise control and good sound production. The right hand can use either a rest stroke or a free stroke to pluck the strings. A rest stroke involves the finger plucking the string and resting on the adjacent string, while a free stroke involves the finger plucking the string and stopping just above the next string.
Here are some tips to help you achieve the best possible sound on your guitar with your right hand:
- Proper hand position: The first step is to ensure that your hand is positioned correctly on the strings. Your right hand should be placed with the fingers curved and resting on the strings just above the soundhole. Your wrist should be slightly angled so that your fingers strike the strings at a perpendicular angle, producing a clear and focused tone.
- Fingernail care: The quality of your fingernails can have a significant impact on the tone you produce. Be sure to keep your nails clean, well-maintained, and at the appropriate length for your playing style. Some players prefer to shape their nails with a file or sandpaper, while others use specialized products like nail hardeners to strengthen and protect their nails.
- Stroke direction: The direction in which you stroke the strings can also impact the sound produced. Aim to stroke the strings in a consistent and controlled manner, with a smooth and even motion. Try experimenting with different stroke directions (i.e. upstroke vs. downstroke) to find the best sound for each passage.
- Rest stroke vs. free stroke: Classical guitarists typically use either rest stroke or free stroke when picking the strings. Rest stroke involves plucking the string and then “resting” the finger on the adjacent string, while free stroke involves plucking the string and then letting the finger move away from the string. Both techniques can produce excellent tone, but they have slightly different characteristics and may be more suited to certain passages or playing styles.
- Dynamics and tone control: Finally, it’s important to pay attention to dynamics and tone control when picking the strings. Use varying levels of pressure and stroke speed to create different dynamic levels and tonal colors. Practice controlling the duration and intensity of each note to create a more nuanced and expressive sound.
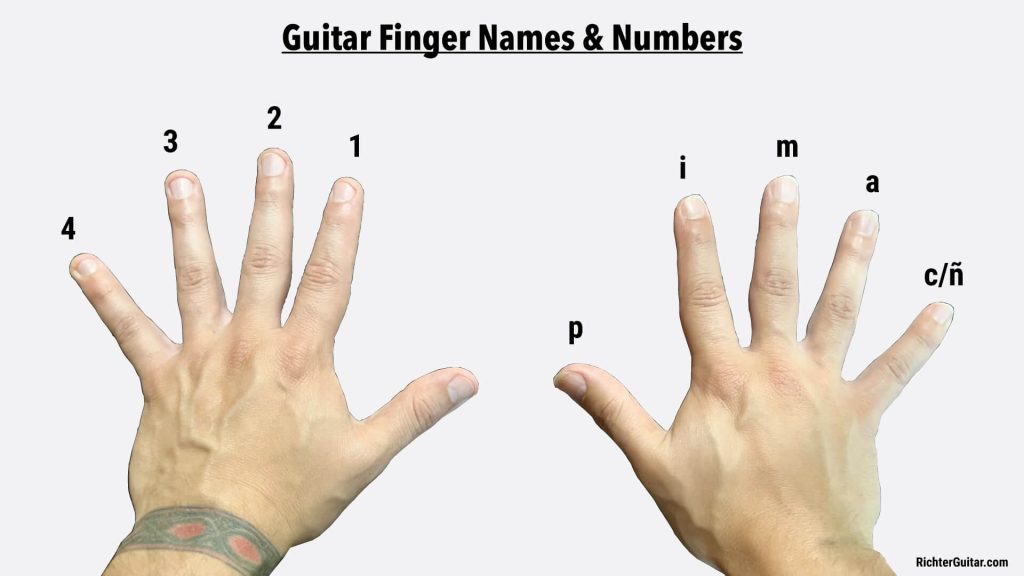

The left hand should be positioned behind the frets, with the fingers coming down perpendicular to the fretboard. The thumb should rest behind the neck of the guitar, providing support and leverage for the fingers. The fingers should press down on the string with the tips, not the pads, to avoid muting other strings. The left-hand fingers should be as close to the fret as possible to ensure proper intonation. Here are some tips to help you get the best sound possible from your instrument:
- Proper finger placement: The first thing to focus on is proper finger placement. Your fingers should be placed just behind the frets, not directly on top of them. This will ensure that the string is pressed down firmly against the fret, producing a clear and resonant sound.
- Pressure and tension: The amount of pressure and tension you use when pressing down on the strings can also affect the sound. Too much pressure can produce a harsh and unpleasant sound, while too little can result in a muted or buzzing sound. Aim for a firm but relaxed grip on the strings, using just enough pressure to produce a clear and sustained tone.
- Finger strength and flexibility: Building up finger strength and flexibility is important for producing a good tone on the classical guitar. Exercises such as scales and arpeggios can help to strengthen the fingers and develop the necessary dexterity to produce clear and fluid playing.
- Finger angle: The angle of your fingers on the fretboard can also impact the sound produced. Aim to keep your fingers at a perpendicular angle to the strings, with the tips of your fingers placed just behind the fret. This will ensure that the string is pressed down firmly against the fret, producing a clear and resonant sound.
- Vibrato: Vibrato is an important technique for adding expressiveness to your playing and enhancing the tone of the guitar. To achieve a good vibrato, start by placing your finger firmly on the string, then use a slight rocking motion to create a subtle variation in pitch. Keep the movement small and controlled, with a consistent rhythm and speed.
By focusing on these key aspects of left-hand technique, you can achieve a beautiful and expressive tone on the classical guitar. It’s important to practice regularly and seek guidance from experienced teachers to continue to improve your playing and develop your own unique sound on the instrument.


Body Technique
Proper body technique is important for playing classical guitar comfortably and avoiding injury. The guitar should be positioned on the left leg, with the footstool supporting the left foot. The guitar should be angled slightly upward, with the neck pointing upward at a 45-degree angle. This position allows for good access to the fretboard and good visibility of the right hand.
The player’s posture is also important, as slouching or leaning too far forward can lead to neck and back pain. The player should sit up straight, with the shoulders relaxed and the feet flat on the floor. The arms should be relaxed, and the elbows should be slightly away from the body.


Guitar Maintenance
Proper guitar maintenance is essential for achieving good tone and preventing damage to the instrument. The guitar should be stored in a case when not in use to prevent damage from humidity and temperature changes. The strings should be changed regularly to ensure good tone and avoid breakage. The fretboard should be cleaned with a soft cloth to remove dirt and oils from the fingers, and the guitar should be polished with a soft cloth to maintain its finish.
Great Sound & Tone
The sound of a classical guitar is a unique and beautiful thing. It can be warm and full-bodied, or bright and sparkling, depending on the technique used and the quality of the instrument.
Choose the Right Strings
The type of strings used on a classical guitar can have a significant impact on its sound. Nylon strings are commonly used for classical guitars, with variations in tension, gauge, and material affecting the sound. High-tension strings can produce a fuller and louder sound, while low-tension strings are softer and more mellow. Carbon or composite strings can produce a brighter and clearer sound, while traditional nylon strings have a warmer tone.
Experiment with different types of strings to find the ones that produce the sound you desire. Keep in mind that the type of strings used can also affect playability, so find a balance between tone and ease of playing.
Pay Attention to Your Fingernails
Classical guitarists pluck the strings with their fingertips, which means the condition of their nails can have a significant impact on the sound produced. Proper nail care is essential for getting the best tone out of a classical guitar.
The fingernails should be filed and shaped regularly to produce a clean and clear sound. The shape of the nail should be slightly rounded, with the sides of the nail sloping down to the center. The length of the nail should be just long enough to produce a clear sound without getting in the way of playing.
Use Proper Technique
Proper technique is crucial for getting the best tone out of a classical guitar. The right-hand technique involves using the fingertips to pluck the strings, with the thumb resting on the bridge of the guitar for support. The left-hand technique involves pressing down on the strings with the tips of the fingers, just behind the frets.
The placement of the right hand on the guitar can also affect the sound produced. Placing the hand closer to the bridge can produce a brighter sound, while placing the hand closer to the neck can produce a warmer tone. Experiment with different hand positions to find the one that produces the desired sound.
Sources
The information in this article is drawn from a variety of sources, including “Classical Guitar Making: A Modern Approach to Traditional Design” by John S. Bogdanovich, a respected luthier, and “Guitar: An American Life” by Tim Brookes, a guitar enthusiast and writer. Other sources include the classical guitar method books by Aaron Shearer and Frederick Noad, as well as online tutorials by professional classical guitarists, such as Jason Vieaux and Ana Vidovic.
In conclusion, getting the best tone out of a classical guitar requires attention to detail and proper technique. By choosing the right strings, caring for your nails, using proper technique, and maintaining your guitar, you can achieve the beautiful and unique sound that the classical guitar is known for. By seeking guidance from experienced teachers and resources, you can continue to improve your tone and enjoy playing classical guitar for a lifetime.

Sources:
The information in this article is drawn from a variety of sources, including “Pumping Nylon” by Scott Tennant, one of the most widely respected guitar technique books. Other sources include the classical guitar method books by Aaron Shearer and Frederick Noad, as well as online tutorials by professional classical guitarists, such as Jason Vieaux and Ana Vidovic. I also was drawing from a variety of sources, including “Classical Guitar Making: A Modern Approach to Traditional Design” by John S. Bogdanovich and “Guitar: An American Life” by Tim Brookes.
Proper technique is crucial for playing classical guitar with precision and beauty. The hand and body positions described in this article, as well as proper guitar maintenance, are key to achieving good tone and avoiding injury. By practicing these techniques regularly and seeking guidance from experienced teachers and resources, guitarists can achieve their full potential and enjoy playing classical guitar for a lifetime.